Microsite
A Microsite is nothing but a customized version of website. They’re built and designed to suit business needs, so they can be as short-term or long-lived, depending on the requirement. Microsites are a great way to promote brands and events — separately from their parent brand/company. They offer great freedom to design the web space according to individual brand characteristics, without any restrictions.
It is a brand-specific website (or a single web page) that companies use to promote their individual products, events, or campaigns. These are hosted on their own domain or company’s subdomain and have a different URL than their company websites. Microsites also give businesses a way to direct specific users to specific sites, built for their specific needs. Mobile banking users, for instance, likely don’t require access to legal documents about trademarks and subsidiaries. They do, however, need to be able to easily log in and check their balance.
Using a microsite, you can launch a product, promotion or campaign in ways that full websites can’t. It eliminates the clutter and distractions that come with a full website. You can use microsites to capture leads that already show an interest towards your product (or service). Such leads have a greater chance of converting into customers.
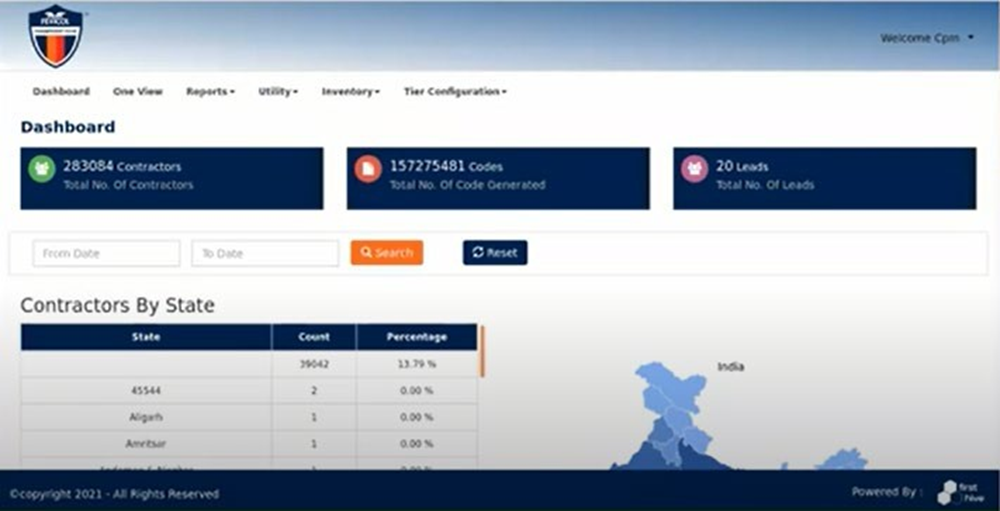
FirstHive’s Take on Microsite
FH builds Microsites based on specific request and scenarios that are explained below:
Scenario 1: If a customer comes to FirstHive and tells I want to build a Customer Care/Call Center software to help my calls to get sort-out quickly when somebody calls the organization. And, if somebody wants to do this, then it will be a part of the microsite. This is something which FH does not make available there or offer as a whole to the customer. This is PS team’s call whether to do that or not, FH won’t support it internally.
Scenario 2: Suppose a customer wants the 19th report to be there and FirstHive does not have that as by default there are only 15 to 18 reports. It comes as a requirement from the client side and FH says it will give the reports of three months from here. However, customer says I need it this week on an urgent basis. There comes the Microsite, where you can get custom reports.
Ideally product extension should back happen there and some called out exceptions that FirstHive is aligned on. FH intend to productize it but not sooner. Survey Module and NPS Module are the prime example. They are the part of the roadmap but not the part of the product solution as of now (may be in 3 or 6 months). |
In Microsite, you have four things:
- Custom Reporting: A Custom Report is a report that you create. You pick the dimensions (City and Browser, for example) and metrics (Sessions, Pageviews, and Bounce Rate, for example) and decide how they should be displayed.
- Custom Hierarchies: Based on hierarchy. It completely depends on PS team, how to implement the hierarchy in Microsite. For example, you have a national sales head under which there are four zones coming in North, East, South, West – from where data is coming. The managers assigned to specific zones will be only able to see the data that is available under their zone and the respective people who works under those managers can only see the data available in that zone.
The hierarchy is not available in FirstHive as default. There are different levels of configuration which are already enabled, some of them need to have specific APIs to be called and parts of it completely DIY. Again, it depends on the customer.
- Custom Dashboarding: Custom dashboards are personalized compilations of reports containing both graphical and list variations of your monitoring data. They are designed to be fully flexible, so you can quickly add report tiles, pick and choose how you display your uptime and performance monitoring data, and spot trends at a glance.
- Custom Workflows: This indicates the workflow. For example, a user comes to the website and clicks, a mail triggered which comes for approval and that goes to the next stage, likewise.
There is no microsite projector CDP product, everything is CDP deployment. The only proper productize solution that we have now is Loyalty. |
Different Terms in CDP Space
Here is a list of terms used in CDP:
| Terms | Description |
| CRM | Ingest data, you have all the records, all new records you create. CRM is basically will only do deterministic fix. CRM can only deal with non-data and is not capable of handling anonymous interaction. Needs email id or mobile to create record/entry, which is the biggest differ between CDP and CRM. The level of customization available in Full stack CDP like FH is different from CRM. The levels and channels are available that are again the function of B2B and B2C. |
| MDM | Marketing data management platform. The type of data FH can ingest tin CDP will vary to that of marketing automation. |
| Data Lake | A single logical store of data that provides a mechanism for storing, accessing, organizing, securing, and managing that data. |
| Data Warehouse | A collection of data copied from company systems, reorganized and often summarized for analysis. |
| Cluster | Also known as compute cluster, workload cluster, or Data Hub cluster. The cluster created by using the Data Hub service for running workloads. A cluster makes it possible to run one or more components and is associated with exactly one data lake. |
| a/b test | A testing method that compares results from two or more test groups whose members are similar except for being given different test treatments. |
| Arbitration | The process of selecting which message to send to an individual who is eligible to receive messages from several separate campaigns. Users must specify the selection criteria (highest immediate value, highest renewal rate, etc.). The decision is usually based on a combination of decision rules and predictive models. |
| Attribution | The process of estimating the revenue (or other measure) caused by a particular marketing contact (or other interaction with a customer). |
| Incremental Attribution | A type of multi-touch attribution that estimates the increase in total revenue resulting from a particular type of marketing contact. |
| Behavioural Data | Data describing individual actions, such as purchases, Web page views, and customer service calls; one person be associated with many behaviours of the same type. |
| Customer Journey | Customer interactions leading up to a specified event, such as a purchase, or interactions across their entire relationship with a company. |
| First Party Cookie | A Web browser cookie set by the domain of the Web site that sets the cookie. |
| First Party Data | Personal data that an organization has acquired directly from an individual. |
| First Touch Attribution | An attribution method that allocates all revenue to the first marketing contact with a customer |
| Fractional Attribution | A type of multi-touch attribution method that allocates specified fractions of total revenue to different marketing contacts based on when they occurred relative to a purchase (first, middle, last). |
| Geotargeting | Targeting of marketing and advertising messages based on the recipient’s location, often in combination with other data known about the individual. |
| Identity Graph | A set of relations among personal identifiers, indicating how each has been linked to the others and which are linked to the same individual. |
| Identity Stitching | The process of connecting a personal identifier to an individual through an intermediary personal identifier (e.g., new device linked to an email address provided by a customer; the device is associated with the customer even though the customer has not herself reported the connection). |
| Journey Orchestration | Coordinating customer treatments over time and across channels, either to achieve a specific purpose (e.g., a marketing campaign with a defined goal) or throughout a company’s relationship with a customer. |
| Offline Data | Data collected by physical interaction such as retail purchases, local events, shipments, etc. |
| Online Data | Data collected by digital systems include Web, mobile apps, smart TVs, etc. |
| Segmentation | Any method that divides an audience into groups of individuals who are in some way similar to each other, typically so they can be treated similarly for marketing purposes |
| Streaming Data | Data received in a continuous flow, such as Web site activity or location history |
| Structured Data | Data that is presented and stored in a fixed format where each element is in a specified location, such as the columns of a relational database table or the fields of a data file. |
| Unstructured Data | Data that is presented and stored in a format where the elements and contents are defined together, as in event logs or key value pairs. |
| Tag Manager | Software that manages Web site tags, typically replacing individual tags with a single tag that captures data required by multiple tags and distributes that data to the appropriate destinations. |
| Third Party Cookie | A Web browser cookie set by a different domain other than the Web site that sets the cookie |
| Third Party Data | Personal data that an organization has acquired through a marketplace relationship with an organization that acquired it directly or indirectly |
| Webhook | A method for communicating between Web systems that sends data to other systems, typically after an event in the originating system (API). |
| Marketing Automation | A software that handles routine marketing tasks without the need for human action. Common marketing automation workflows include email marketing, behavioral targeting, lead prioritization, and personalized advertising. |
