Understanding Events in FirstHive
Firsthive is an intelligent Customer Data Platform that builds unique customer identities by ingesting data from all sources of customer interaction and transactions—such as ERP, CRM, websites, social media, PoS, mobile apps, and customer care platforms.
As the world’s first CDP to apply machine learning for building unified customer identities, FirstHive also layers actionable campaign targeting recommendations to drive a disproportionate increase in marketing ROI.
Since the platform primarily handles data ingestion, unification, and activation, every piece of data flowing in or out impacts system resources—including storage, processing, computation, high availability, and execution channels.
What is an Event in FirstHive? Why Events matter?
An event refers to any data ingested into or sent out from your FirstHive account.
FirstHive’s pricing is based on events, which are directly tied to data movement within the platform. Each data point ingested or pushed from the system counts as an event.
Event counted on data ingestion
When ingesting data, FirstHive creates source identities that capture the context, content, and channel-level attributes of each user interaction. The number of events generated depends on the type of channel and data being tracked.
Each user interaction ingested by FirstHive counts as at least one event. In some cases—such as website tracking—multiple events may be recorded for a single interaction. For example, a user visiting a website counts as one interaction, but every action they take during that session (e.g., page views, clicks, form submissions) is counted as a separate event.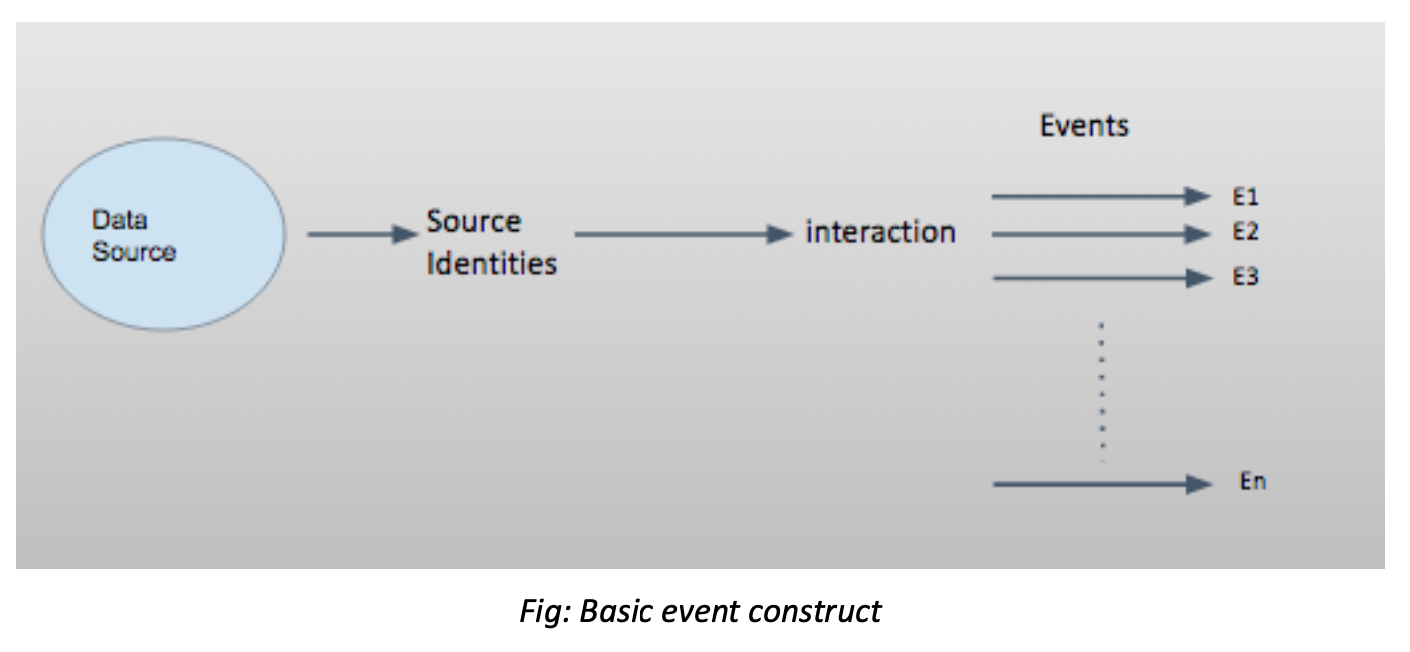
Examples by Source Type
Disclaimer: Following is not an exhaustive list but some of the common or relatable data source types used to explain how events are counted in FirstHive.
- Record-Based Systems (CRM, Data Warehouse, CSV Uploads): Every new record or update—regardless of the integration method (API, JDBC, SFTP)—counts as one event.
- First-Party Interfaces (Website, App, Microsite): Each tracked user action is counted as an event. Example: A user visits the site → lands on homepage → logs in → performs Steps 1–3 → converts = 6 events.
- Third-Party Platforms (Social Media, Chatbots): Every interaction ingested—such as a Facebook “Like” or “Comment”—is counted as an event.
- Campaign Channels (Email, SMS, Voice, Web Push): Events include metrics like “Sent,” “Opened,” “Clicked,” or “Unsubscribed.”
Examples:
- Email: Sent, Opened, Clicked, Unsubscribed
- SMS: Sent, Clicked
- Web Push: Sent, Viewed, Clicked
- API-Connected Channels: Every data record received in response to an API call initiated by FirstHive counts as an event.
Events Counted during Data Activation (Data Out)
FirstHive makes processed data available for activation across various destination channels. These may include campaign tools (email or SMS gateways), audience pushes to platforms like Facebook or Google Ads, call center triggers, data lakes, BI tools, or responses to FirstHive API requests.
Examples by Destination Type:
- Communication Channels: Every message sent from FirstHive (email, SMS, push, etc.) is an event.
- Third-Party Platforms (via Push API): Every record or trigger pushed (e.g., to Facebook, Google Ads, call centers) counts as an event.
- Third-Party Systems (via Request API): Every data packet sent as a response to a data request counts as an event.
- Remote Storage Destinations (SFTP, Data Lakes, BI Tools): Each record pushed to an external storage location is counted as an event.
